Study Results
Datasets including Homogeneous Isotropic Turbulence (HIT) were generated to train surrogate models. Two deep learning architectures, the Fourier Neural Operator and U-Net, were trained to predict a single time step and subsequently multiple time steps via auto-regressive training.
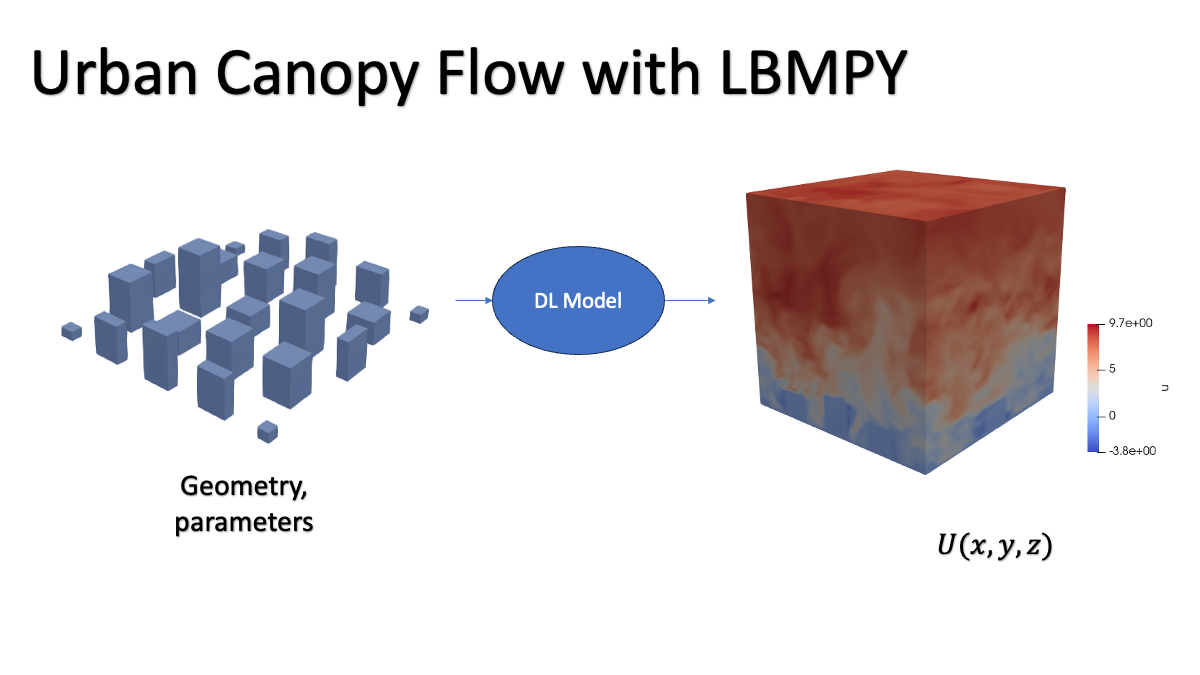
Training surrogate models from large CFD simulations data using our approach through traditional offline learning creates a major bottleneck in network communications which prevents good scalability.
JAX-Fluids : https://jax-fluids.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
A fully-differentiable CFD solver for 3D, compressible two-phase flows, developed with the intention to push and facilitate research at the intersection of ML and CFD.
LBMpy : https://pycodegen.pages.i10git.cs.fau.de/lbmpy/
A python code generation package that supports a wide variety of different lattice Boltzmann methods and generates optimized code for various HPC architectures.
ADIOS2 : https://adios2.readthedocs.io/en/v2.10.2/
A Unified High-performance I/O Framework designed for data exchanges in extreme- scale parallel environment.
Pytorch : https://pytorch.org/
An optimized tensor library for deep learning using GPUs and CPUs.
Benefits
Real-world simulations often require vast amounts of memory. Online training strategies address this challenge by training surrogate models in real time and eliminating the need to store extensive simulation data. In the automotive industry, for example, online training can be integrated with CFD simulations to continuously optimize a vehicle’s aerodynamic performance using wind tunnel and on-road sensor data. This enables designers to dynamically adjust parameters—such as body shape and airflow channels—improving fuel efficiency, reducing drag, and enhancing overall handling.
In the aviation sector, online training can be coupled with digital twins to optimize flight paths based on real-time weather data. Similar benefits extend to manufacturing, where shifting external factors necessitate continuous process adjustments, and to power grid management, allowing for more accurate and efficient energy distribution in response to evolving consumption patterns.
Partners
| CERFACS (www.cerfacs.fr) : Study coordinator. |
| Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (www.fau.eu): Study partner, provider of CFD simulation software. |
Team
- Luciano Drozda
- Nicolas Odier
- Joeffrey Legaux
- Fernando Gonzales
- Harald Koestler
- Shubham Kavane
Contact
Name: Joeffrey Légaux
Institution: CERFACS
Email Address: legaux@cerfacs.fr