Highlights
- Use of graph neural networks provides a way to solve the matrix equation systems using GPUs
- Approximation of SIMPLE algorithm terms that disregarded in the traditional approaches lead to a considerable improvement of performance, accuracy and robustness for several canonical, benchmark and simple Industrial-typical CFD cases
- Exasimple.py code permits all CFD practitioners to reproduce the results here obtained and transfer the major findings to any CFD code
| Keywords | Energy, Environment, Mechanical Engineering, Ocean Sustainability |
Challenge
The use of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has become widespread across many industries, including maritime and offshore renewable sectors. However, the computational cost of CFD simulations remains high, limiting their use in optimisation studies and often requiring simplified modelling. Accelerating CFD codes would allow for more advanced fluid dynamic analyses to be applied in practice.
Current CFD software often suffers from outdated architectural decisions that do not reflect the capabilities of modern massively parallel CPU and hybrid CPU-GPU systems. As a result, they fail to take full advantage of recent hardware advancements, such as those seen in the field of AI. To close this gap, a rethinking of core algorithms is necessary. In particular, integrating machine learning techniques into CFD solvers holds promise, yet remains an underexplored area.
Research Topic
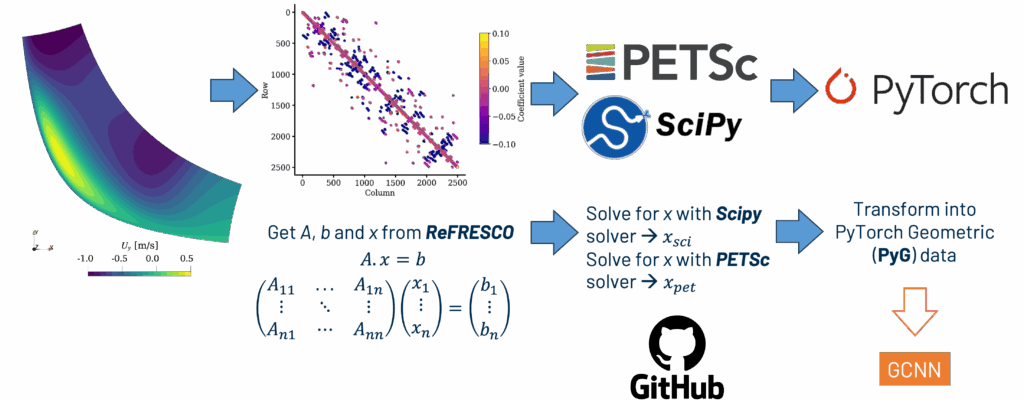
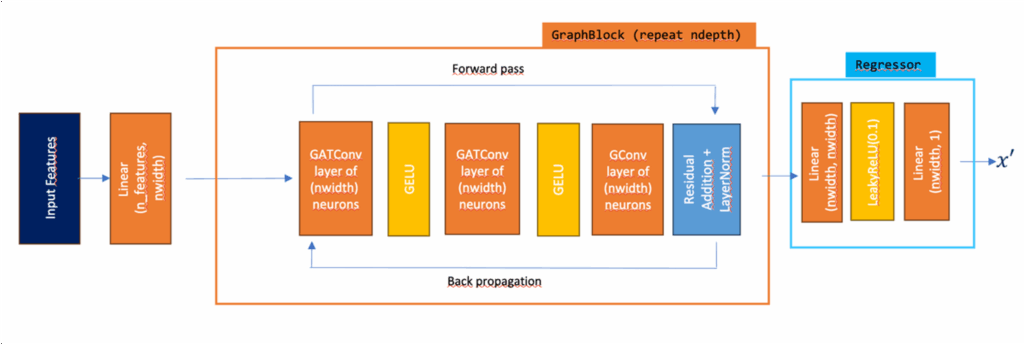
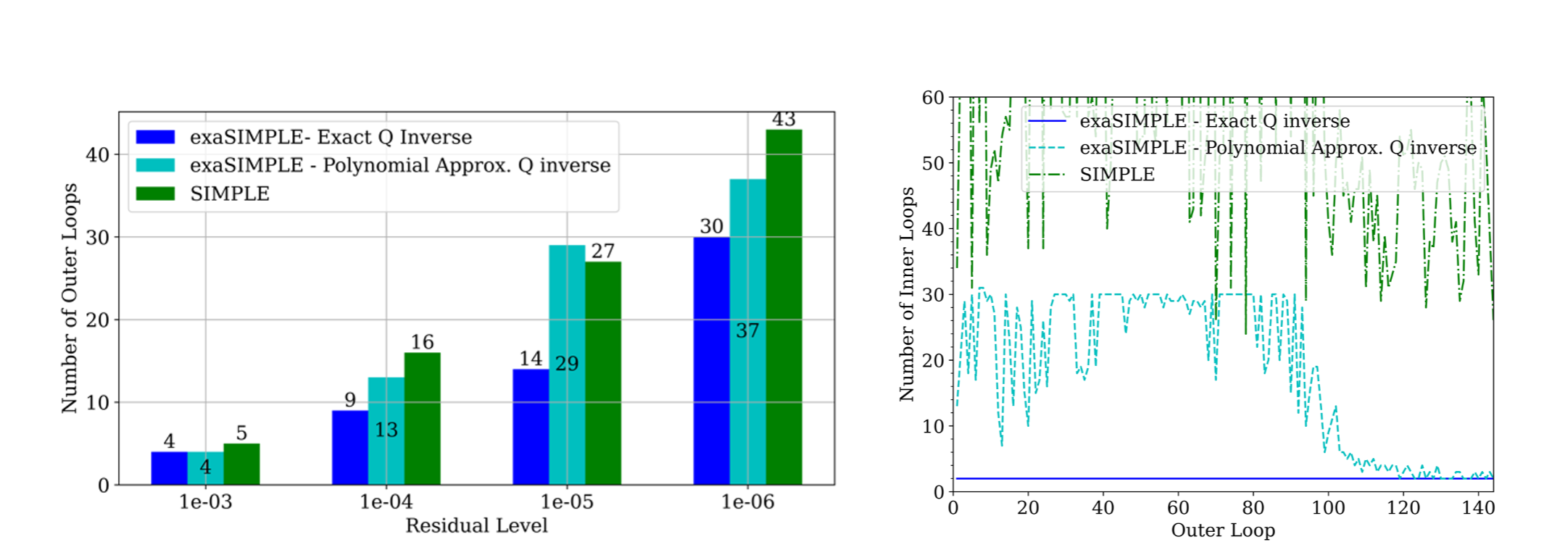
The exaSIMPLE project developed hybrid machine learning-computational fluid dynamic algorithms to enhance the efficiency of CFD solvers. The approach builds upon the SIMPLE algorithm and integrates ML to improve key computational aspects. First, a more efficient way to solve the pressure correction equation is to sought by employing graph neural networks to replace traditional solvers. The approach aims to accelerate CFD codes and enable them to more easily use GPUs. Second, improvements in the pressure-velocity coupling are achieved by lifting a key simplification made in SIMPLE and using ML to approximate a matrix inverse that is typically left out, aiming for faster convergence.
Solution
The adopted solution introduces machine learning models at two critical points within the CFD framework: the pressure-velocity coupling and the linearized equation solver. In both areas, ML is used to infer solutions to computationally demanding sub-problems traditionally addressed using resource-intensive methods.
In the case of pressure-velocity coupling, the ML-enhanced method computes the Navier-Stokes equation solutions more accurately, reducing the number of required iterations and thereby lowering the overall computational cost. For the linear solvers, the solution process is transferred entirely to GPUs, offering better integration with modern computing infrastructure and promising energy savings.
The scientific domain of the exaSIMPLE software lies within ocean, maritime, renewables and naval applications. The technologies employed include the industrial CFD code ReFRESCO (developed and maintained by MARIN and blueOASIS), PETSc libraries for matrix operations and integration of ML solutions, and PyTorch for machine learning model development, particularly for implementing Graph Neural Networks. A new code, exasimple.py, was developed to reproduce the results of this study. All data and code are publicly available through a dedicated GitHub repository:
https://github.com/blueOceanSustainableSolutions/exaSIMPLE