Study Results
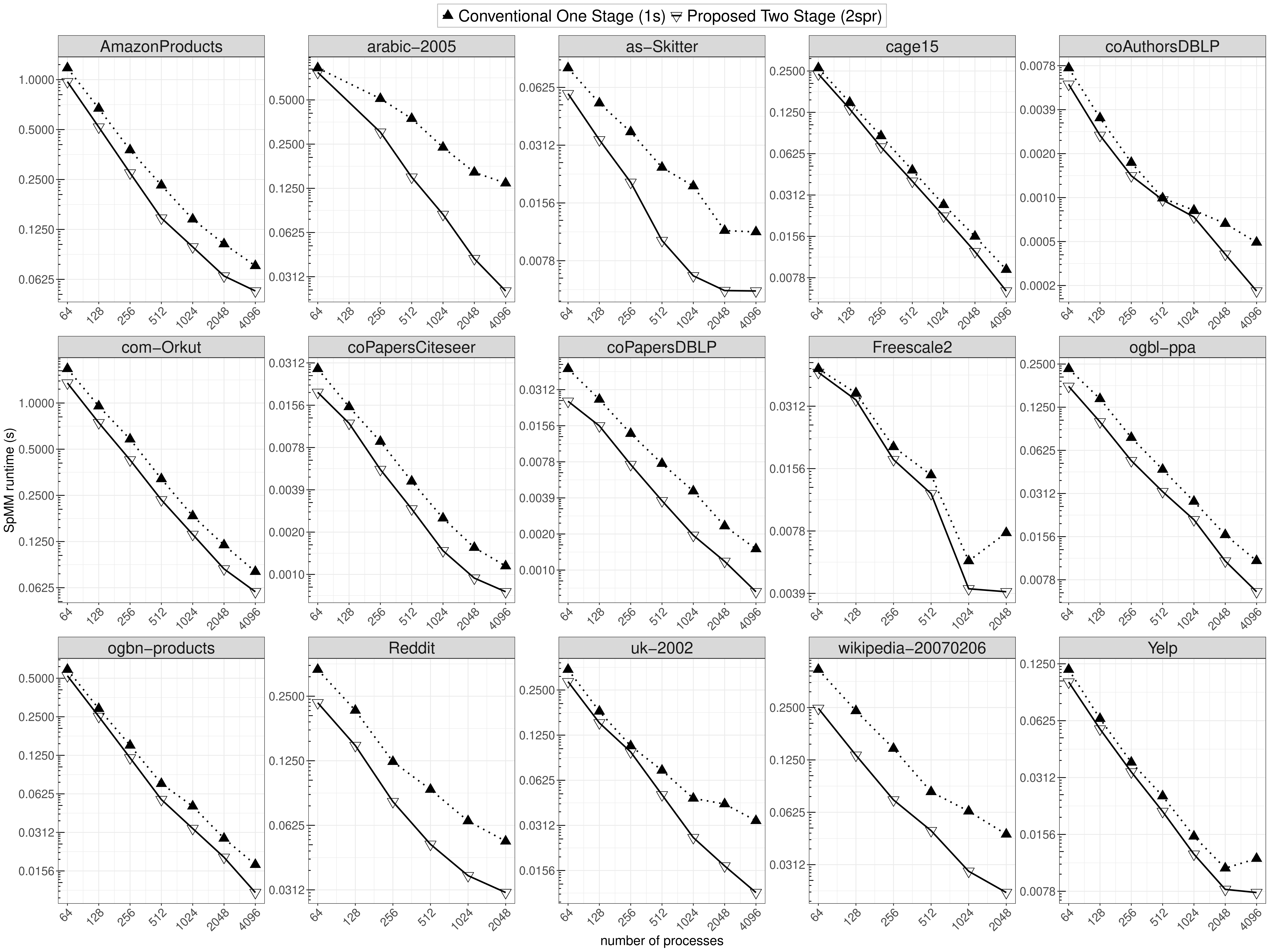
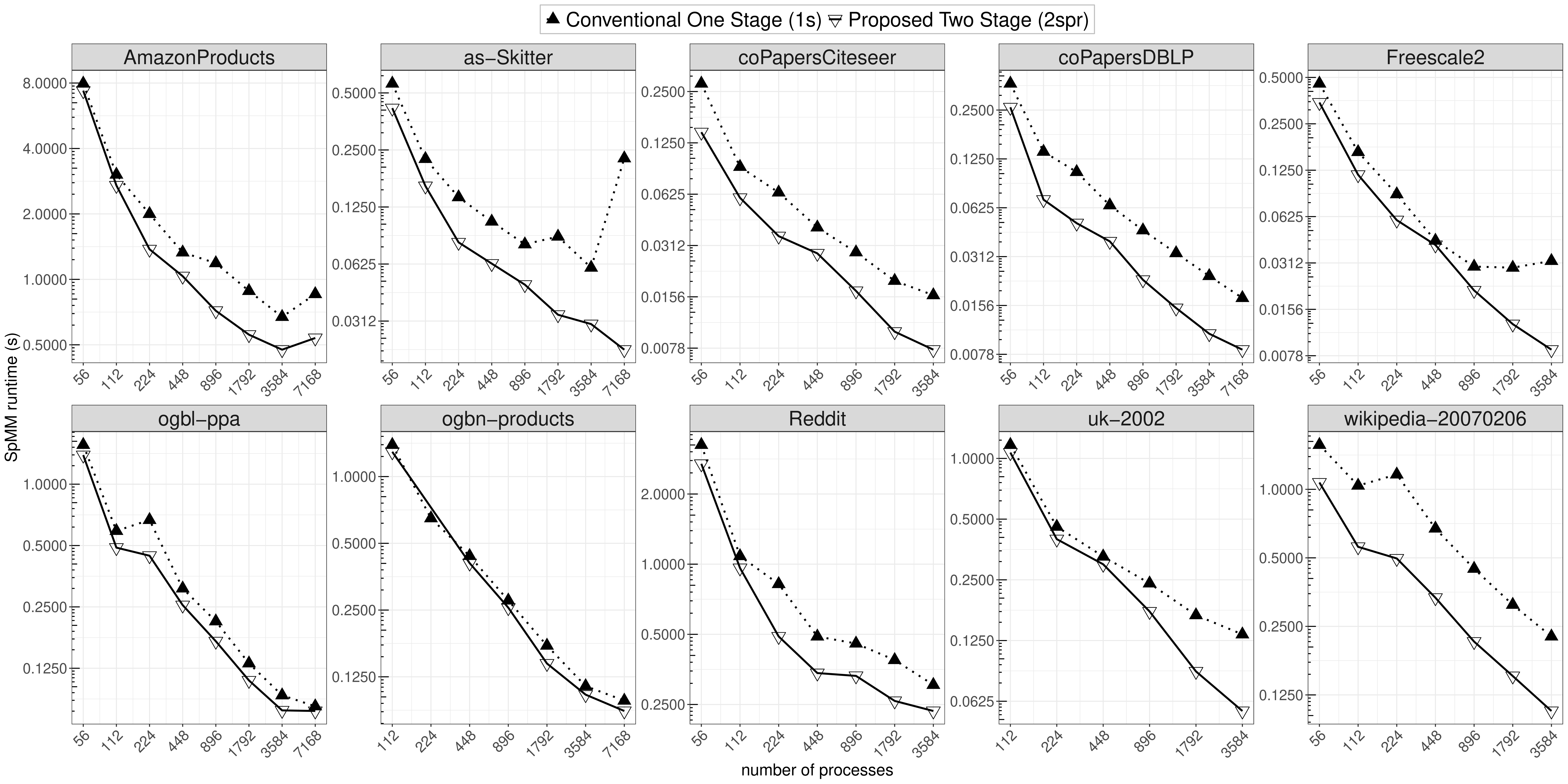
The experimental results reveal that the proposed two-stage communication scheme significantly outperforms the conventional one-stage communication scheme in both communication efficiency and overall runtime. For SpMM workloads on 4096 cores, two-stage achieves up to 93% decrease in maximum communication volume and up to 67% improvement in parallel runtimes compared with one-stage. Furthermore, the two-stage method demonstrates consistently superior scalability in both strong and weak scaling scenarios, exhibiting near-linear weak scaling under increasing process counts and feature dimensions. In GNN training experiments, the two-stage method provides up to 24% decrease in per-epoch training runtime on 2048 cores, confirming its effectiveness in large-scale deep learning tasks. Overall, the framework successfully mitigates communication imbalance in irregularly sparse applications and offers a scalable and portable solution for modern HPC systems.
All codes employed in this project were fully developed in-house by our research group. Both the SpMM and GNN implementations were written in C/C++ and make use of the MPI library to enable scalable distributed-memory parallelism. During the development and testing phases, we extensively utilized the LUMI and MareNostrum 5 systems, as well as the Cray Programming Environment, including its performance analysis and optimization tools. Additionally, we employed the CBLAS library to accelerate local SpMM and Generalized Matrix Multiplication (GeMM) kernel operations within our implementation. Graph partitioning tasks were performed using the METIS tool to achieve load-balanced and communication-efficient partitions. All matrices and graphs used in the experimental evaluation were obtained from the SuiteSparse Matrix Collection and PyG Datasets repositories.
Benefits
The proposed framework unlocks new possibilities by significantly improving the scalability and efficiency of irregularly sparse, bandwidth-bound computations—challenges that were previously limiting the performance of large-scale applications. This advancement in HPC technology particularly benefits fields like graph analytics, machine learning, and scientific simulations, enabling faster and more efficient processing of large, sparse datasets.
In scientific research, the framework facilitates faster processing of massively sparse matrices and graphs, accelerating progress in areas such as computational physics, bioinformatics, and social network analysis. In the industry, the enhanced communication efficiency is crucial for large-scale recommendation systems and fraud detection pipelines, which rely heavily on graph-based models like GNNs. For public administration, applications like urban planning and critical infrastructure modeling, which involve managing complex and irregular datasets, stand to benefit from reduced parallel runtimes and better scalability on modern HPC systems.
Overall, this study delivers a practical and portable communication library that optimizes bandwidth-bound workloads on distributed-memory architectures, offering significant value across scientific, industrial, and public sectors by enabling faster, more efficient, and scalable computations.
Partners
| Bilkent University is actively engaged in high-performance computing (HPC) research, particularly within its Department of Computer Engineering. The university focuses on parallel computing, algorithm optimization, and hardware acceleration.Professor Cevdet Aykanat leads research in parallel scientific computing, emphasizing graph and hypergraph partitioning, load balancing, and scalable algorithms for unstructured applications. His work includes contributions to European HPC initiatives such as PRACE. In applied HPC, Bilkent researchers have developed a message-sharing algorithm that significantly reduces communication overhead in latency-bound parallel applications, achieving an 84% reduction in messages from bottleneck processors. The university also explores heterogeneous computing. PhD research includes developing GPU-accelerated tools for long-read DNA sequencing, enhancing performance in bioinformatics. Additionally, Bilkent collaborates with HAVELSAN in the BiHa Lab, focusing on data science, machine learning, and big data analytics, integrating HPC with real-world applications. Through these initiatives, Bilkent University contributes to advancing HPC methodologies and their practical applications. |
Team
- Prof. Cevdet Aykanat
- Assist. Prof. Hamdi Dibeklioğlu
- Kutay Taşçı
- Can Bağırgan
- Serdar Özata
Contact
Name: Prof. Cevdet Aykanat
Institution: Bilkent University
Email Address: aykanat@cs.bilkent.edu.tr